CN | EN
About Dapuese
More hot topics
2023-01-03
2022/05/16
Manufacturing enterprises widely apply the ANDON system
In many modern manufacturing enterprises, the ANDON system is a very important management subsystem. ANDON, also known as push light, dark light, or an light, is a system widely used in automobile factories. When an abnormality occurs on the production site, it can be promptly intervened by pulling a rope, pressing a button, etc., and notify the responsible person through sound, light, screen, etc. in a timely manner to resolve the issue. Now, let's learn about the widespread application of the ANDON system in manufacturing enterprises.
The ANDON system reflects two management philosophies:
Quality first, even at the cost of emergency stops, exposing problems on the production site for timely resolution. Assembly work is prioritized, with quality engineers, equipment engineers, process engineers, and logistics personnel serving as support staff. This is because the efficiency of the assembly line determines the efficiency of the entire factory.
The following introduces several important factors of the ANDON system.
1. Call
The ANDON system is classified by call type into quality calls, material calls, equipment calls, and line calls. A quality call refers to a call manually triggered by workers pulling a rope or pressing a button when a quality issue arises on site or when workers encounter problems they cannot solve. The initiators of the ANDON system are assembly workers, and the beneficiaries are team leaders and quality engineers. A material call is initiated by workers pressing a material button when they find material shortages. The sender of the ANDON system is the assembly worker, and the recipient is the logistics dispatcher. Each button usually corresponds to a material and integrates with information and logistics execution systems. An equipment call is triggered automatically by the equipment controller when an alarm or fault occurs. The source of the ANDON system is the equipment PLC, and the receiver is the equipment engineer. A line call is automatically triggered by the line controller when an abnormality occurs on the conveyor line.
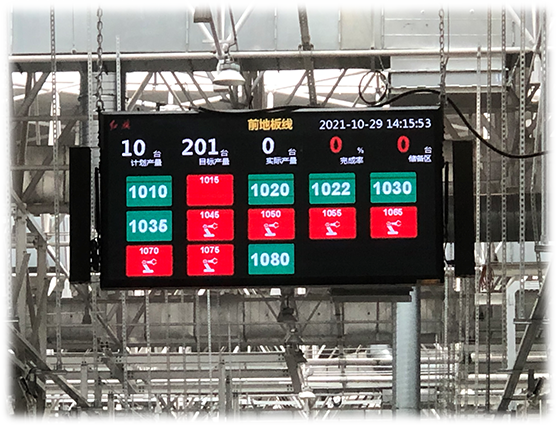
2. Notification
Lights provide notifications in various forms such as sound, light, and screens. Usually, monochrome or tricolor column signal lights are installed at workstations on the production line. Monochrome lights are usually yellow and flash signals to notify when there is a call. Tricolor lights are usually red, yellow, and green, commonly used at main stations such as error-proof stations. Green indicates normal, yellow indicates alarm, and red indicates fault. Signal lights are usually built into the PLC, with a response time within 100ms.
3. Escalation Mechanism
Calls in the ANDON system have levels such as notification, alarm, and fault. If the notification level alternates, there is no abnormality on site when the call is made. Alarm levels, such as material calls, equipment alarms, line shortage, and line blockage, mean the line is still operating when the call is made and will not immediately cause a line stop. Fault levels include equipment faults, line faults, and emergency stops; calls at this level require immediate handling, otherwise the line will stop immediately.
The ANDON system uses conveyor lines for final assembly, with each workstation linked and evenly spaced on the same production line. When the rope is lowered, if the vehicle has not reached 70% of the stop position, the call is at the alarm level. When the vehicle reaches 70% of the stop position and the call has not been responded to, it escalates to the fault level. When the vehicle reaches 90% of the stop position and the call has not been reset, the conveyor line begins to stop. After escalation, the notification forms of sound, light, and screen also change accordingly. For example, the tricolor light flashes yellow during an alarm and flashes red during a fault.

Phone:+86-510-85160390,85160395
Pre-sales/After-sales:+86-133 8289 1299(Engineer Zhu)
Email:zjm@dapuese.com/zwbemail@163.com
Address: No. 10 Hengliang Road, Outang, Huishan District, Wuxi City
Copyright © 2021 Wuxi Dapuese Electronic System Engineering Co., Ltd.